INTRODUCTION
Open interdental spaces and elongated clinical crowns due to increased bone loss in alveolar crest may result from periodontal diseases, ridge resorption, surgeries, trauma, and traumatic tooth extraction.1 Loss of interdental papilla or inadequate marginal and attached gingiva leads to the formation of black triangles in anterior teeth that often creates esthetic and functional clinical problems due to altered labiodental or labioalveolar consonant sound production.2
In cases of severe gingival recession, surgical techniques advocated for gingival recession coverage are technique-sensitive and do not achieve predictable results. Nonsurgical approaches for replacement of missing gingival tissues include removable gingival veneer, gingival flanges retained by precision attachments, and fixed prostheses with gingival-colored ceramics.3 Gingival veneer is a noninvasive yet affective treatment modality for reconstruction of these areas. It may be fixed or removable prostheses used for recreating gingival architecture around recession or alveolar defects that can achieve discernible esthetic results where a large amount of tissue is missing.4
In the present case, prosthetic management of black triangle and recession was done through a removable, pink heat-polymerized acrylic gingival veneer/ Gum Mask / Artificial Gums / Party Gums worn in the labial aspect of the maxillary anterior dental arch.
CASE REPORT
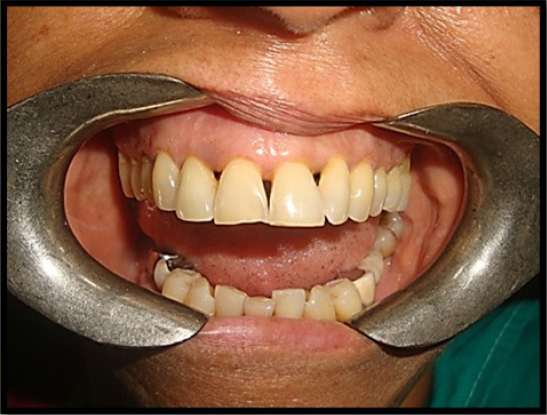
A 47 year old female patient presented with the chief complaint of gaps between her upper front teeth which lead to unpleasant smile (Figure 1). Periodontal assessment revealed gingival recession and probing depths ranging from 4 to 5 mm. Since patient was not willing for surgical treatment, a removable gingival veneer prosthesis was planned to close the spaces between the maxillary anterior teeth.
|
Figure 1: Black triangles between 12,11 21 and 22.
Click here to view |
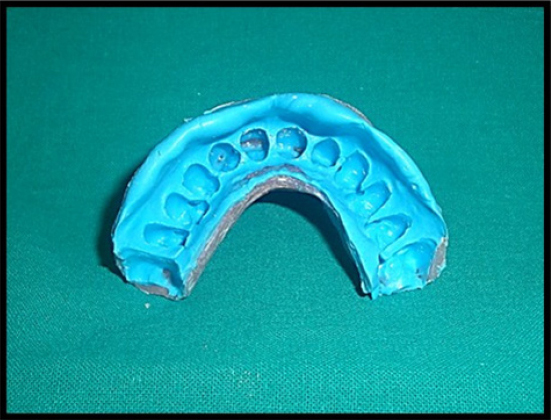
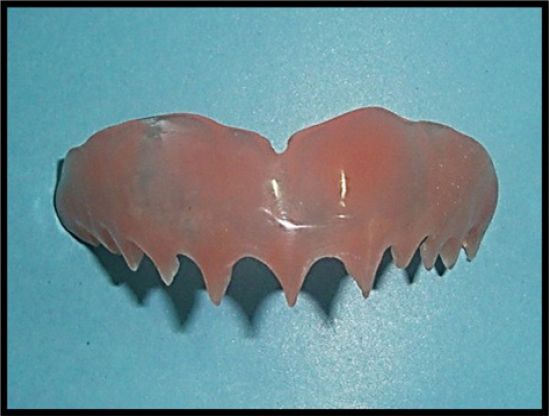
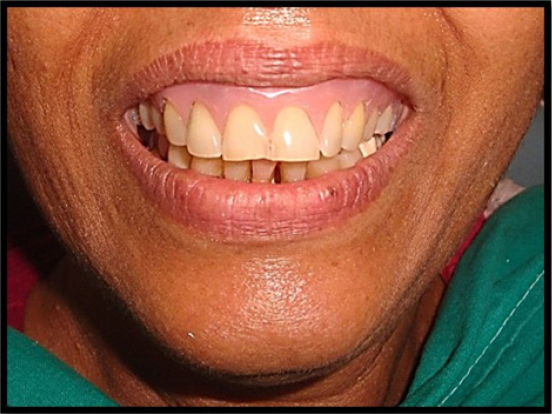
Prior to prosthodontic intervention, scaling and root planning were performed, and oral hygiene instructions were given to the patient. Maxillary primary impression was made using alginate impression material (Tropicalgin, Zhermack, Italy) and diagnostic cast was prepared using type III dental stone (Kalrock, Kalabhai, India). The interdental open gingival embrasures were accurately reproduced in the final impression using addition silicone impression material (Reprosil, Regular Body, Dentsply, USA) in an acrylic custom tray ( DPI, Self-cure, India) that extended from incisal edges to vestibular sulcus in the maxillary anterior region (Figure 2). A wax-up of the prosthesis was prepared involving the undercuts in the master cast (Figure 3) and processed in heat-cured acrylic resin (DPI Heat cure, India) to obtain an extremely thin and flexible gingival veneer (Figure 4). The prosthesis achieved adequate retention by engaging minor interproximal undercuts and pleasingly mimicked the lost soft tissue (Figure 5). Patient was instructed to ensure adequate rest to the gingival tissues and maintain good oral hygiene.
|
Figure 2: Sectional special tray for anterior maxillary impression
Click here to view |

|
Figure 3: Wax-up of gingival veneer.
Click here to view |
|
Figure 3: Wax-up of gingival veneer.
Click here to view |
|
Figure 5: Intraoral view of final prosthesis.
Click here to view |
DISCUSSION
Gingival veneer can be used effectively in interdental defects with > 5 mm gap between contact point and alveolar crest to mask interdental black triangles, exposed root surfaces, and/or crown margins. In addition to improved esthetics and phonetics, this device may be used to prevent root- dentine sensitivity and food packing in interdental spaces.5 It has also been used as a carrier for periodontal dressings, and application of topical medications such as topical fluoride and triamcinolone 0.1% in the treatment of desquamative gingivitis.6
Materials used for the fabrication of gingival veneer prosthesis include auto-cure and heat-cure acrylic resins, copolyamide, composite resins, porcelains, and soft silicone materials.7 The in-vitro color stability, stain resistance, and water sorption of four removable gingival flange materials was studied by Lai et al. wherein gingival flange made of traditional denture base acrylic resins proved to be less prone to staining with coffee and tea than silicone or copolyamide materials.8 However, acrylic materials are hard, rigid, and more prone to fracture in comparison to silicone materials. The silicone prosthesis being more flexible provide better comfort to the patient.
In the present case heat-polymerized acrylic resin was chosen to fabricate the prosthesis due to its easy color matching to adjacent gingival tissues, wide availability and relatively cheaper cost. Furthermore, removable gingival veneer helps to provide adequate rest to the gingival tissues and maintains good oral hygiene. However, poor patient compliance, chances of breakage, high caries activity, acute gingival lesions, food impaction and associated bacterial growth are certain limitations of the prosthesis which require regular supervision by the clinician.
CONCLUSION
Prosthetic management of black triangles through gingival veneer is a simple technique to provide predictable and improved aesthetics in patients who cannot undergo periodontal surgery for the correction of gingival recession. Acrylic-based gingival prosthesis is easy to fabricate, less time consuming and cost-effective treatment modality of gingival replacement.
